diff --git a/docs/usage/administration/understanding_synapse_through_grafana_graphs.md b/docs/usage/administration/understanding_synapse_through_grafana_graphs.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6d6db0ebfe..0000000000
--- a/docs/usage/administration/understanding_synapse_through_grafana_graphs.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,84 +0,0 @@
-## Understanding Synapse through Grafana graphs
-
-It is possible to monitor much of the internal state of Synapse using [Prometheus](https://prometheus.io)
-metrics and [Grafana](https://grafana.com/).
-A guide for configuring Synapse to provide metrics is available [here](../../metrics-howto.md)
-and information on setting up Grafana is [here](https://github.com/matrix-org/synapse/tree/master/contrib/grafana).
-In this setup, Prometheus will periodically scrape the information Synapse provides and
-store a record of it over time. Grafana is then used as an interface to query and
-present this information through a series of pretty graphs.
-
-Once you have grafana set up, and assuming you're using [our grafana dashboard template](https://github.com/matrix-org/synapse/blob/master/contrib/grafana/synapse.json), look for the following graphs when debugging a slow/overloaded Synapse:
-
-## Message Event Send Time
-
-
-
-This, along with the CPU and Memory graphs, is a good way to check the general health of your Synapse instance. It represents how long it takes for a user on your homeserver to send a message.
-
-## Transaction Count and Transaction Duration
-
-
-
-
-
-These graphs show the database transactions that are occurring the most frequently, as well as those are that are taking the most amount of time to execute.
-
-
-
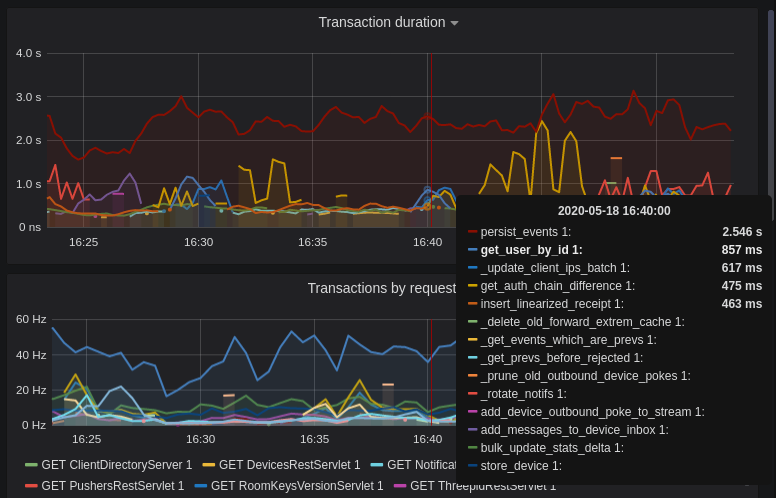
-In the first graph, we can see obvious spikes corresponding to lots of `get_user_by_id` transactions. This would be useful information to figure out which part of the Synapse codebase is potentially creating a heavy load on the system. However, be sure to cross-reference this with Transaction Duration, which states that `get_users_by_id` is actually a very quick database transaction and isn't causing as much load as others, like `persist_events`:
-
-
-
-Still, it's probably worth investigating why we're getting users from the database that often, and whether it's possible to reduce the amount of queries we make by adjusting our cache factor(s).
-
-The `persist_events` transaction is responsible for saving new room events to the Synapse database, so can often show a high transaction duration.
-
-## Federation
-
-The charts in the "Federation" section show information about incoming and outgoing federation requests. Federation data can be divided into two basic types:
-
-- PDU (Persistent Data Unit) - room events: messages, state events (join/leave), etc. These are permanently stored in the database.
-- EDU (Ephemeral Data Unit) - other data, which need not be stored permanently, such as read receipts, typing notifications.
-
-The "Outgoing EDUs by type" chart shows the EDUs within outgoing federation requests by type: `m.device_list_update`, `m.direct_to_device`, `m.presence`, `m.receipt`, `m.typing`.
-
-If you see a large number of `m.presence` EDUs and are having trouble with too much CPU load, you can disable `presence` in the Synapse config. See also [#3971](https://github.com/matrix-org/synapse/issues/3971).
-
-## Caches
-
-
-
-
-
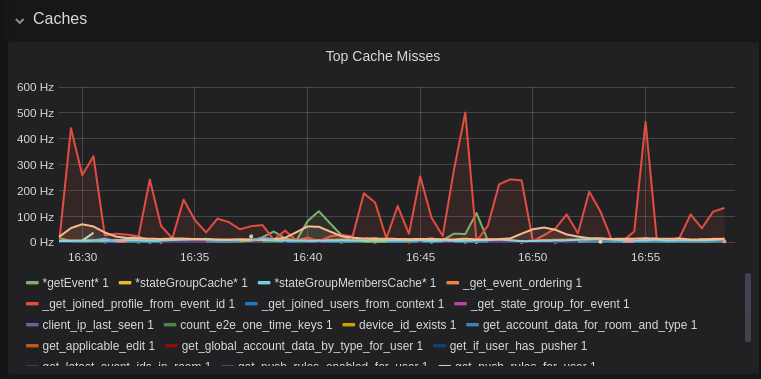
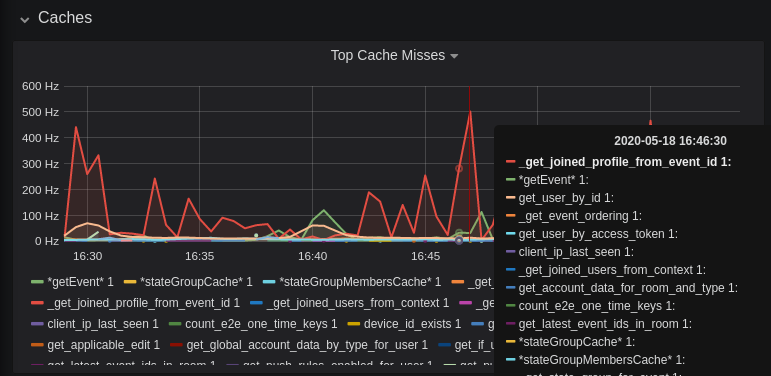
-This is quite a useful graph. It shows how many times Synapse attempts to retrieve a piece of data from a cache which the cache did not contain, thus resulting in a call to the database. We can see here that the `_get_joined_profile_from_event_id` cache is being requested a lot, and often the data we're after is not cached.
-
-Cross-referencing this with the Eviction Rate graph, which shows that entries are being evicted from `_get_joined_profile_from_event_id` quite often:
-
-
-
-we should probably consider raising the size of that cache by raising its cache factor (a multiplier value for the size of an individual cache). Information on doing so is available [here](https://github.com/matrix-org/synapse/blob/ee421e524478c1ad8d43741c27379499c2f6135c/docs/sample_config.yaml#L608-L642) (note that the configuration of individual cache factors through the configuration file is available in Synapse v1.14.0+, whereas doing so through environment variables has been supported for a very long time). Note that this will increase Synapse's overall memory usage.
-
-## Forward Extremities
-
-
-
-Forward extremities are the leaf events at the end of a DAG in a room, aka events that have no children. The more that exist in a room, the more [state resolution](https://spec.matrix.org/v1.1/server-server-api/#room-state-resolution) that Synapse needs to perform (hint: it's an expensive operation). While Synapse has code to prevent too many of these existing at one time in a room, bugs can sometimes make them crop up again.
-
-If a room has >10 forward extremities, it's worth checking which room is the culprit and potentially removing them using the SQL queries mentioned in [#1760](https://github.com/matrix-org/synapse/issues/1760).
-
-## Garbage Collection
-
-
-
-Large spikes in garbage collection times (bigger than shown here, I'm talking in the
-multiple seconds range), can cause lots of problems in Synapse performance. It's more an
-indicator of problems, and a symptom of other problems though, so check other graphs for what might be causing it.
-
-## Final Thoughts
-
-If you're still having performance problems with your Synapse instance and you've
-tried everything you can, it may just be a lack of system resources. Consider adding
-more CPU and RAM, and make use of [worker mode](../configuration/workers.md)
-to make use of multiple CPU cores / multiple machines for your homeserver.
-
|
